Wisdom traditions from ancient civilizations have long provided guiding principles for ethical conduct, governance, and justice. Despite the passage of time, the insights and values embodied in these philosophical traditions remain relevant and applicable to contemporary challenges in the pursuit of justice. In this exploration, we’ll delve into various ancient wisdom traditions and their enduring relevance to modern concepts of justice.
Ancient Wisdom Traditions
Ancient civilizations across the globe developed sophisticated philosophical systems that explored the nature of justice, morality, and the human condition. These wisdom traditions continue to inspire contemporary thought and discourse on ethics and governance.
1. Ancient Greek Philosophy
- Philosophers: From Socrates and Plato to Aristotle, ancient Greek philosophers delved into questions of justice, virtue, and the ideal society.
- Concepts: Ideas such as justice as fairness (Plato’s Republic), virtue ethics (Aristotle’s Nicomachean Ethics), and the social contract (Socrates’ dialogues) continue to shape ethical discourse.
2. Confucianism
- Confucius: Confucianism, originating in ancient China with the teachings of Confucius, emphasizes moral cultivation, social harmony, and ethical governance.
- Principles: Key concepts such as ren (benevolence), li (ritual propriety), and xiao (filial piety) inform Confucian notions of justice and moral virtue.
3. Hinduism
- Dharma: In Hindu philosophy, the concept of dharma encompasses moral duty, righteousness, and cosmic order, guiding individuals in their ethical conduct and social responsibilities.
- Laws of Manu: The Laws of Manu (Manusmriti) delineate principles of justice, social hierarchy, and legal governance within Hindu society.
4. Buddhism
- Noble Eightfold Path: Buddhism advocates for ethical conduct, compassion, and mindfulness as integral to the pursuit of enlightenment.
- Right Action: The concept of right action (samma kammanta) emphasizes moral integrity and ethical behavior in all aspects of life, including governance and social justice.
Relevance to Modern Justice
The insights and principles embedded in ancient wisdom traditions offer valuable perspectives on justice that resonate with contemporary concerns and challenges.
1. Human Dignity and Equality
- Universal Values: Wisdom traditions emphasize the inherent dignity and worth of every individual, underscoring the importance of treating all people with fairness, respect, and compassion.
- Social Justice: Concepts such as equality before the law and the fair distribution of resources reflect foundational principles of justice across cultures and traditions.
2. Ethics in Governance
- Leadership Ethics: Ancient wisdom traditions provide guidelines for ethical leadership, emphasizing virtues such as integrity, humility, and service to the community.
- Just Governance: Ideas of just governance, informed by principles of wisdom and virtue, call for leaders to prioritize the common good and uphold principles of fairness and equity.
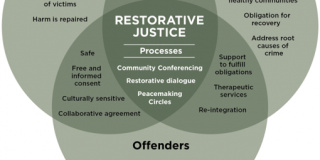
3. Restorative Justice
- Healing and Reconciliation: Wisdom traditions offer insights into restorative justice practices focused on healing, reconciliation, and repairing harm within communities.
- Forgiveness and Compassion: Concepts of forgiveness, compassion, and empathy play a central role in restorative justice approaches that seek to address the root causes of conflict and harm.
Applying Ancient Wisdom in Modern Contexts
Drawing upon the insights of ancient wisdom traditions, modern justice systems and policymakers can incorporate ethical principles and values into their decision-making processes.
1. Ethical Education and Training
- Curriculum Integration: Integrate teachings from ancient wisdom traditions into educational programs and training initiatives for legal professionals, policymakers, and leaders.
- Ethical Reflection: Encourage individuals to engage in ethical reflection and self-examination, drawing upon timeless wisdom to inform their moral decision-making.
2. Policy Development and Reform
- Human-Centered Policies: Develop policies and legislation that prioritize human dignity, equity, and justice, guided by the ethical principles of ancient wisdom traditions.
- Community Engagement: Foster dialogue and collaboration with communities to co-create solutions that align with cultural values and promote social cohesion.
3. Global Dialogue and Exchange
- Cross-Cultural Understanding: Facilitate cross-cultural dialogue and exchange to promote mutual understanding and appreciation of diverse ethical perspectives and traditions.
- Shared Values: Identify shared values and principles across wisdom traditions to foster collaboration and solidarity in addressing global challenges and promoting justice.
Conclusion: Bridging Past and Present
As we navigate the complexities of modern justice, we can draw inspiration and guidance from the timeless wisdom of ancient traditions. By incorporating ethical principles, virtues, and insights from diverse cultural and philosophical perspectives, we can forge a path toward a more just, equitable, and compassionate society. In honoring the legacy of ancient wisdom, we enrich our understanding of justice and strengthen our collective commitment to upholding human dignity, fairness, and integrity for generations to come.