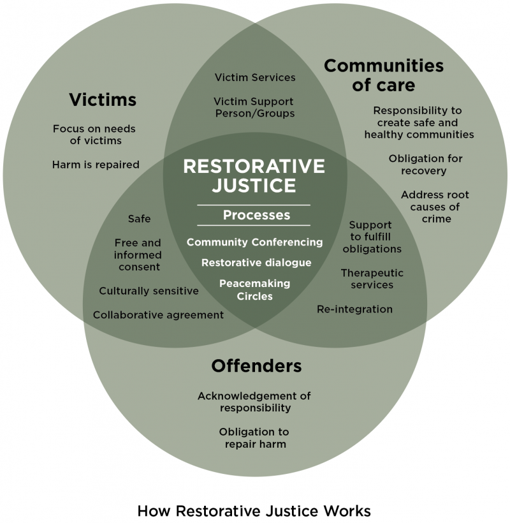
Restorative justice is a transformative approach to addressing harm and conflict within communities, prioritizing healing, accountability, and reconciliation over punishment and retribution. By fostering empathy, dialogue, and collaboration, restorative justice seeks to repair the harm caused by wrongdoing and build stronger, more resilient communities. In this exploration, we’ll delve into the principles and practices of restorative justice, highlighting its profound impact on individuals, families, and societies.
Understanding Restorative Justice
Restorative justice is grounded in the belief that crime and conflict harm not only individuals but also communities and relationships. Instead of focusing solely on punishment, restorative justice centers on repairing harm and restoring relationships through inclusive processes of dialogue, empathy, and accountability.
1. Healing and Reconciliation
- Emotional Restoration: Restorative justice acknowledges the emotional and psychological impact of harm, offering opportunities for healing and closure for victims, offenders, and affected communities.
- Rebuilding Trust: By fostering open communication and empathy, restorative justice helps rebuild trust and repair fractured relationships, strengthening the social fabric of communities.
2. Accountability and Responsibility
- Personal Accountability: Restorative justice holds individuals accountable for their actions, encouraging them to take responsibility for the harm they have caused and make amends to those affected.
- Community Responsibility: Restorative justice also recognizes the collective responsibility of communities in preventing and addressing harm, promoting a sense of shared accountability and mutual support.
Principles of Restorative Justice
Restorative justice is guided by core principles that emphasize respect, inclusion, and collaboration in the pursuit of justice and healing.
1. Respect for Dignity
- Human-Centered Approach: Restorative justice respects the inherent dignity and worth of all individuals involved, treating them with empathy, compassion, and respect.
- Active Listening: Practitioners engage in active listening and empathy, creating safe spaces for participants to share their experiences and perspectives without judgment.
2. Inclusive Participation
- Community Involvement: Restorative justice processes involve affected parties, including victims, offenders, and community members, in decision-making and problem-solving.
- Empowerment: By empowering stakeholders to actively participate in the resolution process, restorative justice promotes ownership and accountability for outcomes.
3. Repairing Harm
- Restitution and Restoration: Restorative justice seeks to repair the harm caused by wrongdoing by addressing the needs and interests of those affected and facilitating meaningful restitution or restoration.
- Addressing Root Causes: Beyond addressing immediate harm, restorative justice aims to identify and address underlying causes of conflict and injustice, fostering long-term systemic change.
Practices of Restorative Justice
Restorative justice encompasses a variety of practices and interventions designed to facilitate healing, reconciliation, and resolution.
1. Victim-Offender Mediation
- Facilitated Dialogue: Victim-offender mediation brings together victims and offenders in a facilitated dialogue to discuss the impact of the offense, address underlying issues, and negotiate reparative actions.
- Empathy Building: Through dialogue and reflection, participants develop a deeper understanding of each other’s perspectives and experiences, fostering empathy and mutual respect.
2. Circle Processes
- Community Circles: Circle processes bring together affected parties and community members in a circle format to share stories, discuss concerns, and collaboratively develop solutions.
- Shared Values: Circles are guided by values such as respect, honesty, and equality, creating a supportive environment for dialogue, consensus-building, and conflict resolution.
3. Restorative Conferencing
- Multi-Party Dialogue: Restorative conferencing involves a facilitated dialogue among victims, offenders, supporters, and stakeholders to address harm, repair relationships, and develop a plan for moving forward.
- Collaborative Decision-Making: Participants work together to identify needs, explore solutions, and agree on actions that promote accountability, restitution, and healing.
Impact and Benefits of Restorative Justice
Restorative justice has been shown to have transformative effects on individuals, families, and communities, promoting healing, resilience, and social cohesion.
1. Victim Empowerment
- Voice and Agency: Restorative justice gives victims a voice and agency in the resolution process, empowering them to express their needs, seek validation, and participate in decision-making.
- Closure and Healing: By acknowledging the harm they have experienced and engaging in meaningful dialogue with offenders, victims often report increased feelings of closure, satisfaction, and emotional healing.
2. Offender Rehabilitation
- Personal Transformation: Restorative justice encourages offenders to confront the impact of their actions, take responsibility for their behavior, and make amends to those they have harmed.
- Reduced Recidivism: Studies have shown that participation in restorative justice processes is associated with lower rates of reoffending, as offenders gain insight into the consequences of their actions and develop empathy for others.
3. Community Cohesion
- Social Bonds: Restorative justice strengthens social bonds and trust within communities by fostering connections, empathy, and cooperation among diverse stakeholders.
- Conflict Resolution Skills: Through participation in restorative justice processes, community members develop conflict resolution skills, resilience, and a sense of collective responsibility for maintaining peace and harmony.
Conclusion: Building a Restorative Society
Restorative justice offers a compassionate and effective alternative to traditional punitive approaches, promoting healing, reconciliation, and accountability within communities. By embracing principles of respect, inclusion, and collaboration, societies can build a restorative justice system that prioritizes human dignity, empathy, and social justice for all. Through ongoing education, advocacy, and implementation of restorative practices, we can create a more compassionate and resilient society where conflicts are resolved with understanding, compassion, and a commitment to healing.